Currently, the demand for transporting goods requiring low-temperature preservation is increasing. To meet this need, insulated trucks have become a popular choice. However, many people still confuse insulated bodies and refrigerated bodies. So, what exactly is an insulated truck body, and how does it differ from a refrigerated body? This article from Xe Tai My Dinh experts will provide detailed information and help you better understand insulated trucks.
What is an Insulated Truck Body?
An insulated truck body, also known as a thermal insulated body, is a type of truck body specifically designed to maintain a lower internal temperature than the external environment. The key feature of an insulated body is its superior thermal insulation capability, which helps limit heat exchange between the inside and outside of the truck body. The materials used to construct insulated bodies are typically materials with good insulation properties such as polyurethane, composite, or insulating foam.
The main purpose of using insulated trucks is to transport and preserve temperature-sensitive goods such as fresh vegetables, fruits, fresh flowers, medicines, vaccines, processed foods, and other medical products. Insulated bodies help keep goods fresh, ensure quality, and extend their shelf life.
 Insulated truck transporting fresh produce
Insulated truck transporting fresh produce
Comparing Insulated and Refrigerated Truck Bodies
Although both insulated and refrigerated bodies aim to preserve goods at low temperatures, there are fundamental differences in their function and construction:
Refrigerated Truck Bodies
Refrigerated truck bodies are designed to preserve goods at freezing temperatures, typically below 0°C (32°F), and can even reach -18°C (-0.4°F) or lower depending on the preservation requirements of specific goods. To achieve these temperatures, refrigerated bodies are equipped with specialized refrigeration units. These units are capable of deep cooling and maintaining stable temperatures inside the truck body, even when traveling long distances and in harsh weather conditions.
Refrigerated bodies are commonly used to transport frozen foods such as meat, fish, seafood, ice cream, pre-prepared frozen meals, and other specialized medical products requiring extremely low preservation temperatures.
 Refrigerated truck transporting ice cream
Refrigerated truck transporting ice cream
Key Differences
The biggest difference between insulated and refrigerated bodies lies in the cooling system. Insulated bodies rely solely on the insulation capability of the materials to maintain the existing temperature, while refrigerated bodies actively cool down and maintain low temperatures using a refrigeration unit.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Insulated Truck Body | Refrigerated Truck Body |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Maintain cool temperature, cold preservation | Deep cooling and maintain freezing temperature |
| Temperature | Typically above 0°C (32°F) | Typically below 0°C (32°F) (can go down to -18°C (-0.4°F) or lower) |
| Refrigeration Unit | None or can be additionally equipped (optional) | Mandatory specialized refrigeration unit |
| Application | Transporting goods requiring cool preservation | Transporting frozen goods |
| Goods | Vegetables, tubers, fruits, flowers, medicines, … | Meat, fish, seafood, ice cream, frozen foods, … |
Construction of Insulated Truck Bodies
The construction of insulated truck bodies is designed with multiple layers to optimize thermal insulation. Typically, a high-quality insulated body will include the following layers:
- Outer shell: Usually made of composite, aluminum, or stainless steel, with load-bearing, impact-resistant, and waterproof capabilities.
- Inner wall: Similar to the outer shell, can use composite, aluminum, or stainless steel, ensuring hygiene and easy cleaning.
- Insulation layer: This is the most important layer, determining the insulation capability of the body. The common insulation material is polyurethane foam (PU foam) with appropriate thickness, ensuring optimal insulation efficiency.
- Moisture barrier layer: Prevents moisture from penetrating the insulation layer, maintaining long-term insulation capability and protecting goods from mold and mildew.
- Floor: Usually reinforced with stainless steel or load-bearing materials, with drainage grooves for easy cleaning.
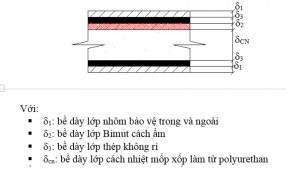 Multi-layer construction of an insulated truck body
Multi-layer construction of an insulated truck body
Insulated Body Materials: Composite and Aluminum
The materials for constructing insulated truck bodies are diverse, but the most common are composite and aluminum. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Composite Insulated Bodies
Advantages:
- Superior insulation: Composite has excellent insulation capabilities, helping the truck body maintain stable temperatures and save cooling energy (if applicable).
- Absolutely waterproof: Not affected by water and moisture, protecting goods from damage due to mold and mildew.
- High durability: Good load-bearing capacity, impact resistance, long lifespan.
- Aesthetics: Smooth surface, easy to shape and paint, providing a modern and professional appearance.
Disadvantages:
- High cost: Higher initial investment cost compared to other materials.
- Difficult to repair when severely damaged: If a large panel is broken due to a strong impact, repairs can be complex and costly.
Aluminum Insulated Bodies
Advantages:
- Reasonable cost: The cost of building aluminum bodies is usually lower than composite.
- Lightweight: Helps reduce vehicle weight, saving fuel.
- Easy to repair: Aluminum is easy to process and repair when damaged.
- Aesthetics: Shiny surface, providing a clean appearance.
Disadvantages:
- Lower insulation capability than composite: Requires a thicker insulation layer to achieve equivalent effectiveness, which may reduce cargo space.
- Prone to corrosion: Aluminum can corrode over time, especially in humid environments or when exposed to chemicals.
Conclusion
Insulated trucks are an effective cold chain transportation solution for many types of products. Although they do not have the deep freezing capability of refrigerated trucks, insulated bodies still well meet the cool preservation needs for items such as vegetables, fruits, flowers, and medicines on short and medium journeys.
Choosing between an insulated body and a refrigerated body depends on the type of goods to be transported and specific temperature preservation requirements. If you need to transport frozen goods, a refrigerated body is the optimal choice. Conversely, if you need to transport chilled goods, an insulated truck will be a more economical and effective solution.
For detailed advice on insulated truck models and to choose the most suitable option for your transportation needs, please contact Xe Tai My Dinh immediately via hotline 0984373720. We are always ready to assist you!